Nuclear Fusion
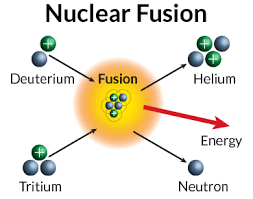

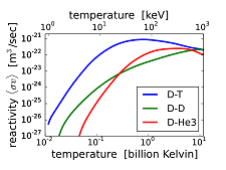
What is Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is the reaction where light atoms when they combine to create heavier elements. The difference in energy between before and after the fusion is released as huge amounts of energy. Active stars in the solar system use this process to produce massive amounts of energy in the form of heat and light. LIghter elements are more easier to fuse because they overcome the repelling force of same charges in the nucleus.
History Behind Nuclear Fusion
In the 1930s, scientists figured out nuclear fusion was possible to recreate, and that it was the main source of energy of stars. In the 1940s, scientists began looking for ways to harness the energy of fusion reactions into a weaponized bomb during the Manhattan Project. However, the hundreds of millions of degrees Fahrenheit required to sustain this reaction was too hot for any container to hold at the time. After the 1960s, the US and Russia worked together to research fusion reactions and deemed it not to be used as a weapon.
Uses of Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion can be used for many practical purposes that can benefit our everyday lives. For instance, nuclear power can be used as a more efficient way to produce electricity. Nuclear fusion can provide safer and cleaner energy compared to its fission counterpart. The fuel required to power nuclear fusion, deuterium and tritium, both derivatives of hydrogen, are found in abundant amounts on Earth. NASA is also trying to use fusion power to power deep-space rockets because there would be an essentially infinite fuel supply because hydrogen and its derivatives are so abundant.